Considering the situation of pests, diseases and weeds in fields and gardens, the need to use pesticides is considerable. Considering the cost of using pesticides, it is essential to identify the correct techniques for their use. The following items will help to increase the effectiveness of agricultural pesticides:
1. The first and most important step is to correctly identify the pest and consult with herbal medicine experts to determine the type of pesticide needed.
2. Pre-knowledge methods should be used to determine the time of spraying.
3. Using pesticides at the right time (according to the growth period of the plant and the life stages of the pest or weeds).
Most pesticides can only control certain stages of the life of pests. For example, many insecticides only affect the larval stage. Others target only adult insects or only eggs. Many fungicides have prophylactic properties, and if the disease has started and intensified, it may not be controlled. Some herbicides should be used pre-emergence and others post-emergence. Also, in the use of herbicides, the multi-leaf weed is important in determining the time of spraying.
4. To carry out spraying operations, especially in crops, in order to determine the amount of water consumed per hectare, the sprayer must be calibrated. Things such as the type of nozzle, the speed of the tractor, the pressure of the output solution for calibration should be taken into consideration. For example, the best type of nozzle for spraying in agriculture is the T-jet 8002 nozzle, whose spraying angle is 80 degrees, and its overlap is better than other nozzles. If the spraying angle is higher, the overlapping will not be done well.

5. Foliar spraying time of pesticide is very important, it is better to do foliar spraying in cool weather in the early morning or in the evening so that the absorption of elements by the leaves is more efficient and at the same time it does not cause leaf burns. For example, in spraying pistachio orchards, foliar spraying should be done when the tree is not thirsty, in other words, foliar spraying should be done before or a few days after irrigation. In pistachio farming areas, where the irrigation cycle is usually long, this matter should be paid special attention and the foliar spraying program should be adjusted so that it is as close as possible to the irrigation time of the gardens. When using herbicides, pay attention to the fact that the field is not under drought stress because it plays a major role in the effect of the herbicide. You may even need to irrigate the field before applying the herbicide, so be sure to follow the instructions on the pesticide label.
6. If you use a common sprayer for spraying, be sure to wash all parts of the sprayer well before spraying, because the small residue of pesticides may also cause burning in the product and the effectiveness of insecticides, fungicides or affect the next herbicide.
7. Do not use pesticides more than the recommended limit in one season.
8. It is necessary to use appropriate equipment for spraying operations (mask, hat, rubber gloves, protective glasses, long and sleeved clothes, rubber boots).
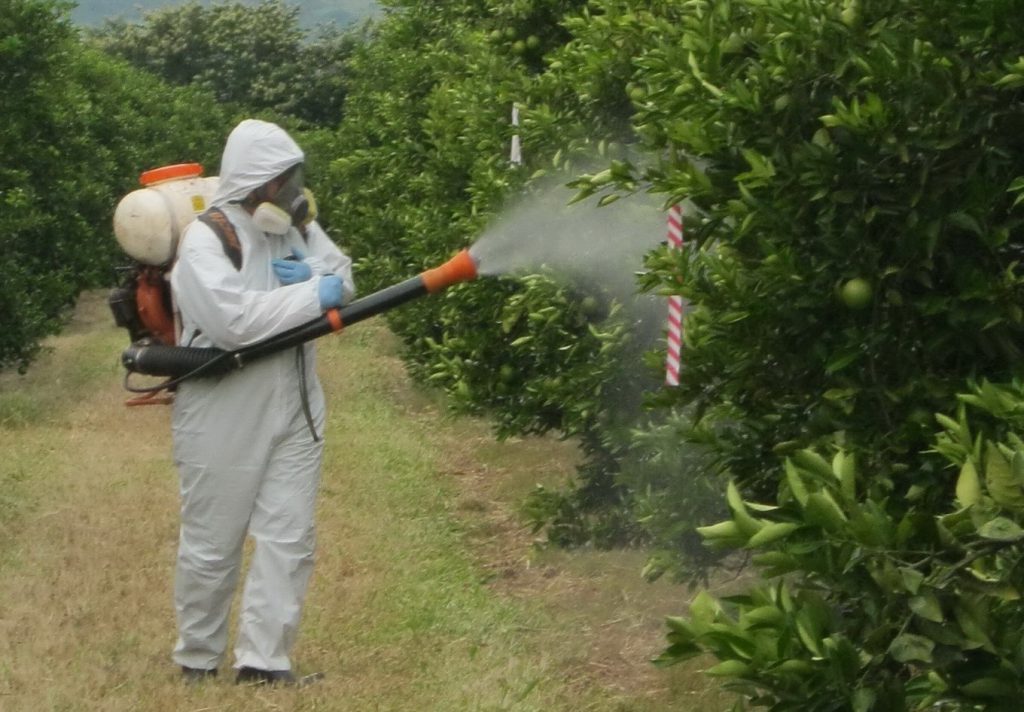

9. The use of pesticides should be strictly in accordance with the dosage recommended on the product label.
10. Do the spraying operation when there is no wind, in case of a light wind, spray against the wind.
11. Air humidity is effective on the evaporation rate of pesticides. Usually, a relative humidity of more than 45% is recommended for spraying operations. Low humidity causes the pesticide drops to evaporate quickly, and in these conditions wind blowing occurs more.
12. To dilute toxins, the degree of water hardness should be taken into account, because hard water has alkaline properties and will reduce the effect of toxins. Also, the salinity of the water should be according to the standard. Waters that contain suspended substances or are muddy are not recommended for use with pesticides.
13. If it rains immediately after the spraying operation, the poison drops will be washed off the plant, which will reduce the effect of the pesticide. Therefore, when choosing the time of spraying, the weather should be considered.
14. In using pesticides with similar resistance group, follow the rotation.
15. Spraying on days when the air temperature is over 28 degrees Celsius should be avoided.
16. Never add thick chemicals to an empty tank, first fill half of the tank with clean water and then add pesticide and finally fill it up with the required water.
17. Mixing incompatible poisons with each other, as well as mixing poisons with fertilizers, in addition to affecting their effect, sometimes also causes plant burn. Therefore, it is recommended not to do this, if for some reason it is necessary to do the mixing operation, before that, be sure to consult with the herbal medicine expert in your area and before spraying on a wide area, first do the mixing test on a small area. .
If the instructions related to the use of pesticides are implemented correctly, pest control will be carried out accordingly. In addition, unwanted side effects for humans, animals and the environment will be minimized.
:References
- 1. Bohmont, B. The Standard Pesticide User’s Guide. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs
- 2. Marer, P. 1988. The Safe and Effective Use of Pesticides. Univ. Of California. Statewide IPM project
- C. A. Wilen, UC IPM Statewide Program, San Diego County; D. L. Haver, UC Cooperative Extension, Orange County; M. L. Flint, UC Statewide IPM Program, Davis; P. M. Geisel, UC Cooperative Extension, Fresno County; and C. L. Unruh, UC Cooperative Extension, Fresno County. Produced by University of California Statewide IPM Program
Preparation and compilation
Sara Mehrabi – technical officer